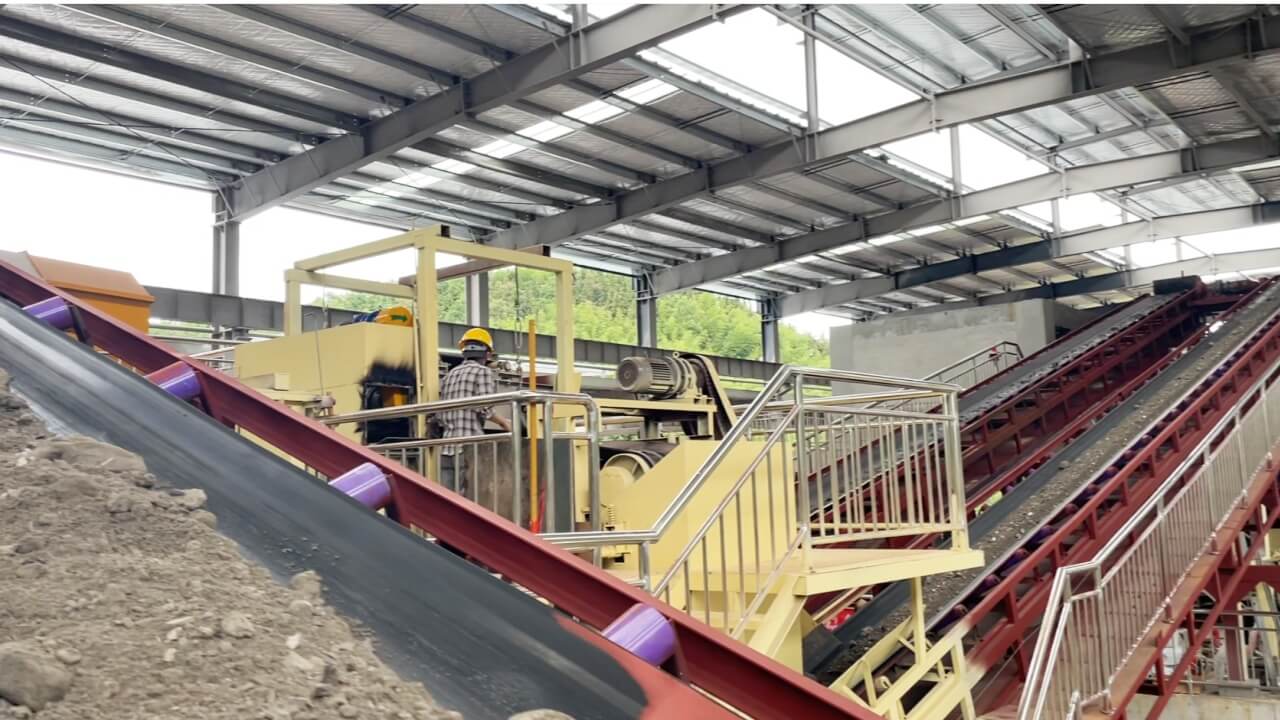
After a month of intensive work, the Hangzhou Incineration Bottom Ash (IBA) Wet Sorting Project located in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, was successfully completed and put into operation. This production line with processing capacity of 1000t/d is designed for sorting and recover the ferrous, non ferrous metal and other valuable resources. It’s a significant breakthrough in waste management technology and sustainable resource utilization.

Significance of IBA Wet Sorting Solution
Environmental Impact
Incineration bottom ash (IBA), a by-product of municipal solid waste incineration, contains metals, glass, and inert substances. Without proper treatment, it can release heavy metals and pollutants into soil and water, posing environmental risks.
Technological Significance Impact
Wet sorting technology addresses these issues by separating IBA components based on density, size, and shape. This reduces hazardous waste volume and recovers valuable resources, promoting the circular economy. By preventing landfill disposal of reusable materials, the project conserves natural resources and minimizes environmental impact.
Economic Value of IBA Wet Sorting Project
Through IBA wet separation process, valuable metals such as iron, aluminum, and copper can be recovered from the incineration bottom ash.
Market Value of the Recovered Metals
The following table shows the international market prices of valuable metals recovered from IBA as of 2025:
| Metal | International Recovery Price (Approximate, per Kilogram) |
| Iron | Around $0.31 |
| Aluminum | Approximately $2.2 – $2.5 |
| Copper (Common Bright Copper) | Up to $9.8 – $10.1 |
| Copper (Motor Copper) | Around $8.4 – $9.1 |
These recovered metals, once refined, can be sold in the international market, creating a major revenue source.
Besides metal recovery, the project produces high – quality inert materials. These can substitute for construction aggregates, reducing the demand for virgin materials and offering a cost – effective option for the construction industry. Transforming waste into resources offsets operational costs and paves the way for sustainable waste management business models.
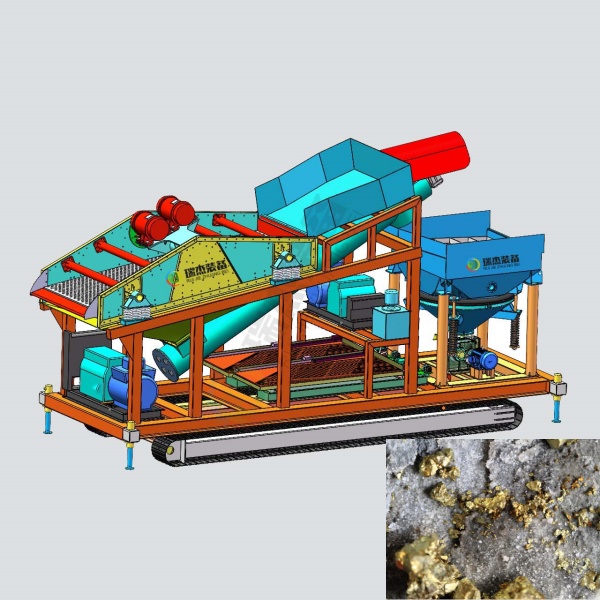
Functions of Each IBA Production Line Equipment
- Uniform Feeding System:
Reciprocating feeders ensure continuous and consistent material flow to the conveyor belt, optimizing downstream processing efficiency. - Conveyor Belt System:
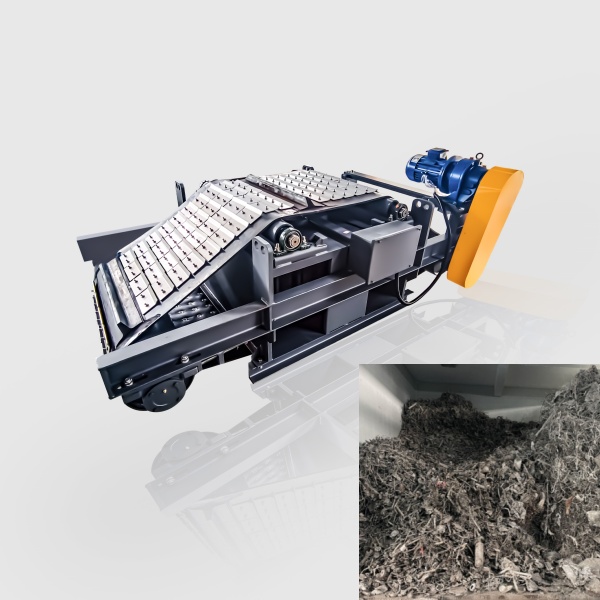
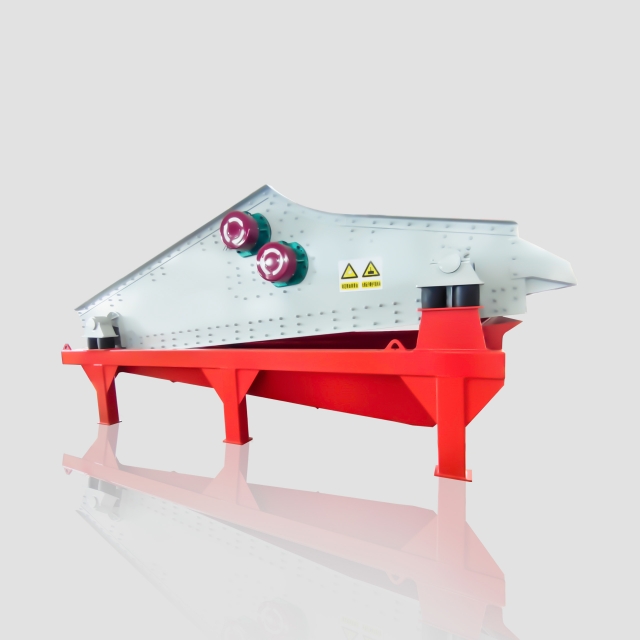
Transports materials to various processing units while maintaining controlled speed and flow rate. - Grading Drum Screen:
Separates materials into different particle sizes through trommel screen, enabling precise classification. - Electromagnetic Overband Separator:
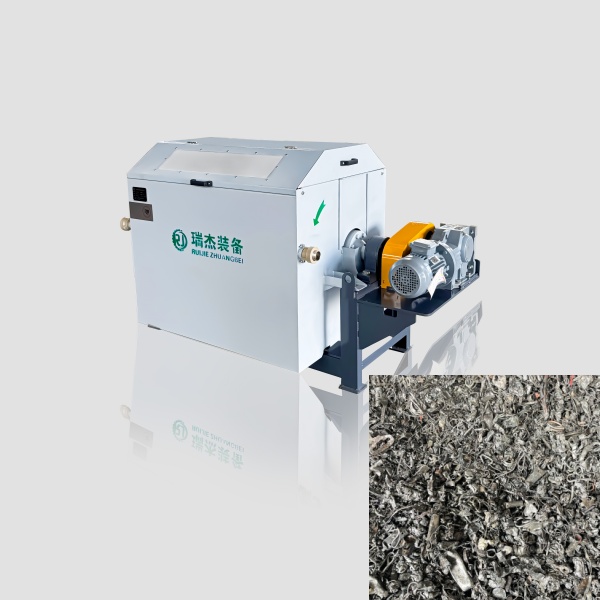
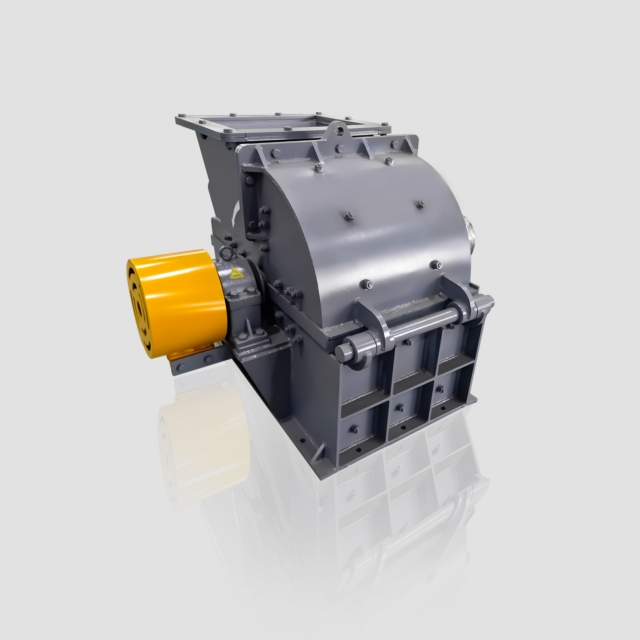
Removes large ferrous metals and non-ferrous metals via powerful magnetic fields, protecting downstream equipment. - Hammer Crushers:
Processes oversized iron scraps, stones, and aggregates into desired particle sizes for further separation. - Magnetic Separation Machines:
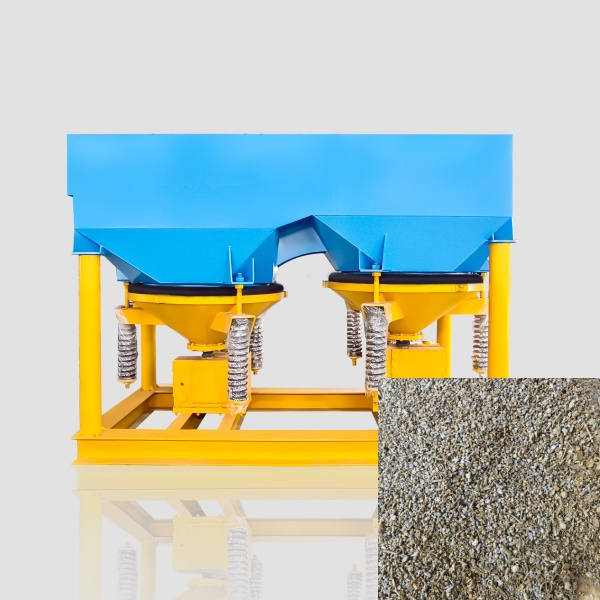
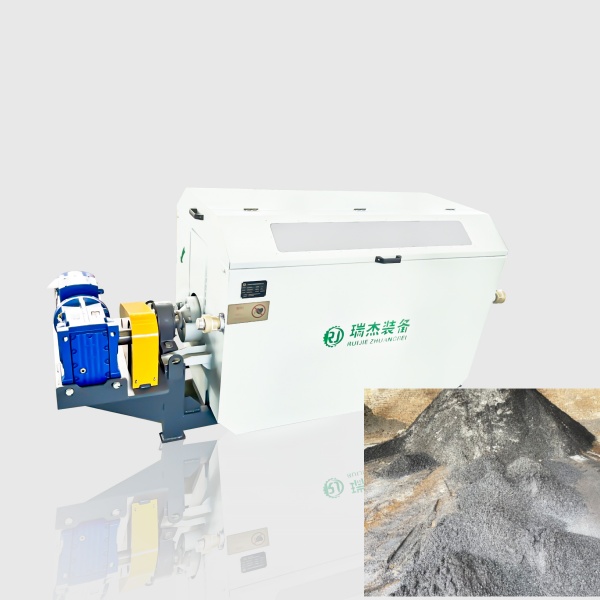
Combines wet drum magnetic separators, up-suction magnetic separators, and magnetic trommel screen to recover ferrous metals of varying sizes. - Jig Separator:
Utilizes gravity-based separation principles to grading and sorting non-ferrous metals, precious metals, and rare earth elements. - Sand Washing Machine:
Cleans and removes impurities from sand particles, producing high-quality construction-grade sand. - Aluminum Separation System:
Employs eddy current separators to precisely extract aluminum from mixed materials, achieving high-purity aluminum recovery. - Shaking Table Combined with Permanent Magnetic Separator:
Specialized for recovering fine-grained non-ferrous metals in powder form through combined density and magnetic separation.

All equipment on the entire production line is interconnected and operates efficiently, ultimately achieving a high recovery rate, zero emissions, and zero pollution.
The Vital Factors for Equipment Selection
When to select the right equipment for your project, you may consider the following aspects :
- Material Characteristics: Properties of the materials to be processed (e.g., particle size, density, abrasiveness).
- Capacity: Required throughput volume (e.g., tons per hour).
- Target Resources: Specific materials intended for recovery (e.g., metals, aggregates).
- Facility Layout: Available floor space and spatial constraints of the plant.
- Budgetary Constraints: Capital expenditure and long-term operational costs.
- Performance Objectives: Desired recovery rates, purity levels, and environmental compliance.
- This structured approach ensures optimal equipment configuration tailored to project-specific requirements.
Future Development Directions of Ruijie Equipment
In the future, Ruijie Equipment will continue to strengthen its technical team by recruiting top talent and introducing cutting-edge technologies. By integrating the specific requirements of various industries, we aim to develop more efficient, intelligent, energy-efficient, durable sorting equipment and a wide range of related resource recovery machinery.
In conclusion, the Hangzhou IBA Wet Sorting Project sets a new standard in waste management. With its environmental and economic advantages, along with Ruijie’s continuous development, it serves as a model for future initiatives worldwide.